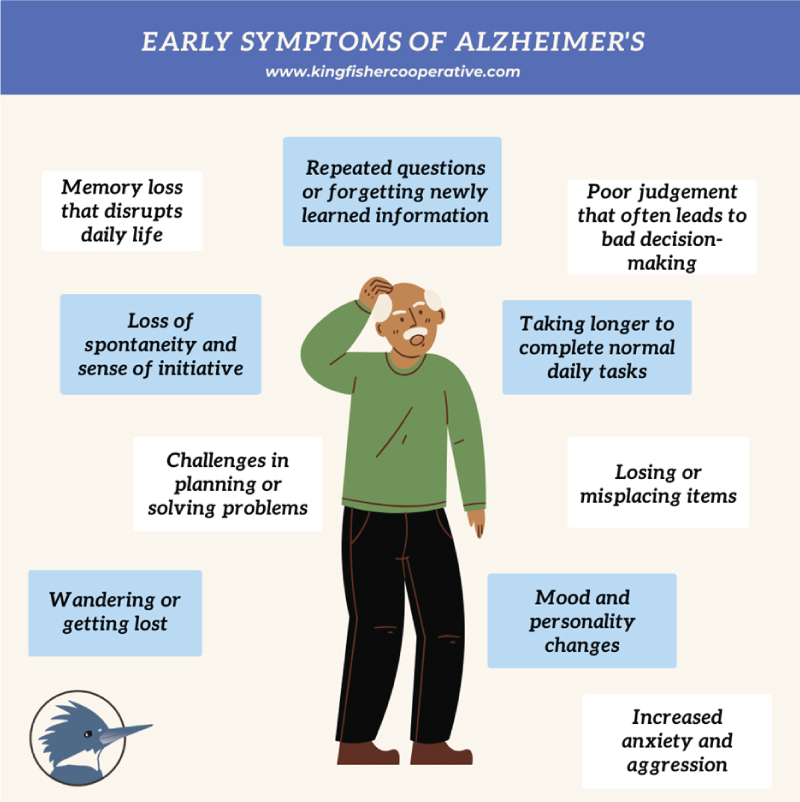
Memory loss: Memory loss is forgetfulness without impairment in function.
Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): Mild cognitive impairment involves cognitive impairments beyond those expected based on an individual’s age and education, but which are not significant enough to interfere with most activities of daily living. MCI may occur as a transitional stage between normal aging and dementia, especially in Alzheimer’s disease.
Dementia: Dementia is a term used to describe a range of conditions affecting the brain that worsen over time. It is the loss of the ability to think, remember, and reason to levels that affect daily life and activities. Some people with dementia cannot control their emotions and other behaviors, and their personality may change. Dementia isn’t a disease. It’s a symptom of brain disorders that negatively impact cognitive function. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common reason why people develop dementia but certainly is not the only cause of dementia.
- Involves parts of the brain that control thought, memory, and language.
- It is the most common type of dementia.
- Age is the best-known risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease.
- A healthy lifestyle may help reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
- Researchers believe that genetics may play a role in developing Alzheimer’s disease.
- It can seriously affect a person’s ability to carry out daily activities.
- Alzheimer’s is a progressive disease.